Introduction to Deep Learning
1. What is a neural network?
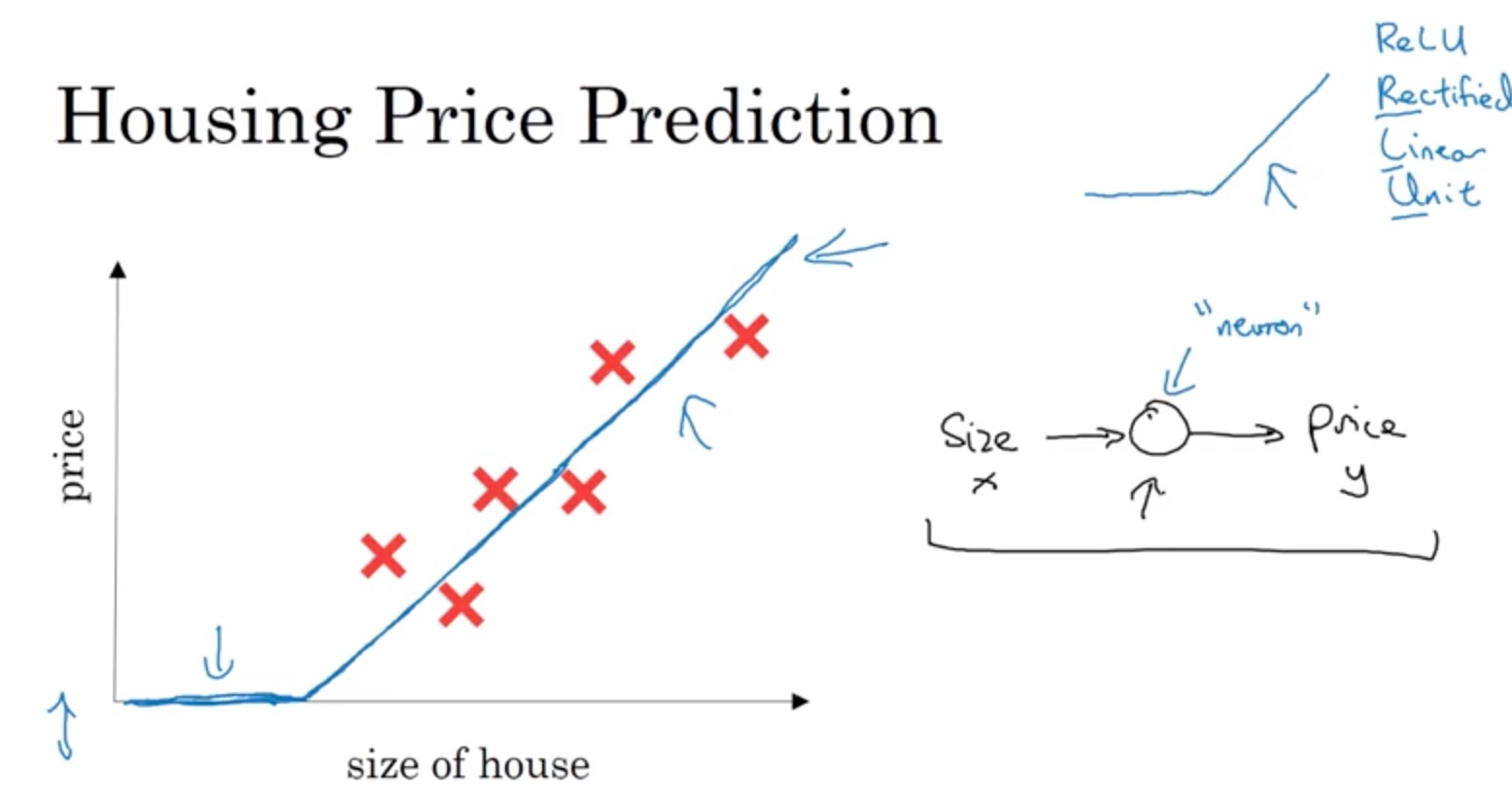
课程中通过“Housing Price Prediction”的例子说明了什么是神经网络。
神经元:处理若干个数据输入,输出一个处理结果的元件。模仿生物神经元,故称神经元。根据数据处理方式有很多种神经元。如
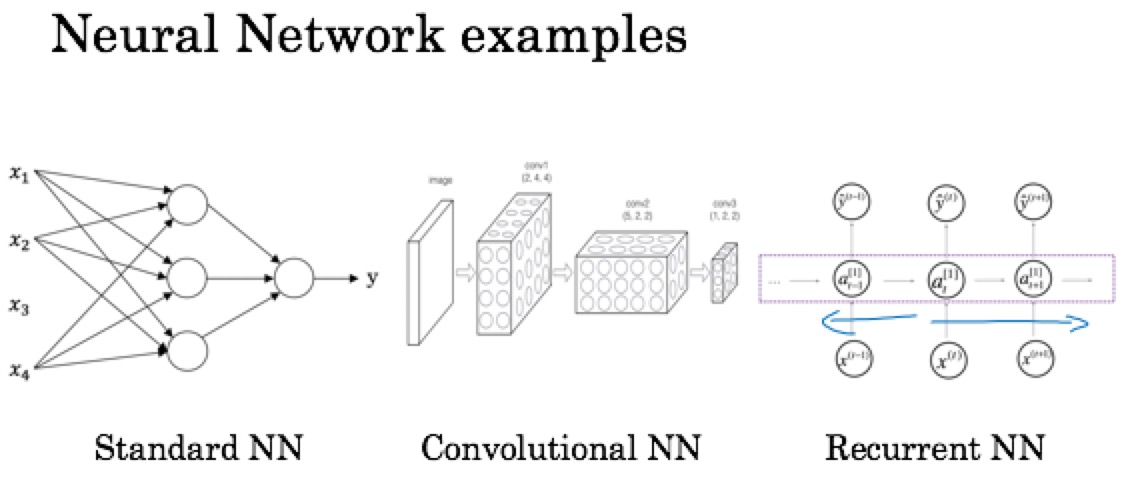
神经网络:若干个神经元组成的数据处理网络。类似于生物神经网络。由一个输入层(Input layer)、一个输出层(Output layer)、若干个隐藏层(Hidden layer)组成。
2. Supervised Learning with Neural Networks
我更喜欢 Jason Brownlee 的定义。
The majority of practical machine learning uses supervised learning.
Supervised learning is where you have input variables (x) and an output variable (Y) and you use an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to the output.
The goal is to approximate the mapping function so well that when you have new input data (x) that you can predict the output variables (Y) for that data
It is called supervised learning because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process. We know the correct answers, the algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training data and is corrected by the teacher. Learning stops when the algorithm achieves an acceptable level of performance.
Supervised learning problems can be further grouped into regression and classification problems.
Classification: A classification problem is when the output variable is a category, such as “red” or “blue” or “disease” and “no disease”.
Regression: A regression problem is when the output variable is a real value, such as “dollars” or “weight”.
与监督学习对应的是无监督学习(Unsupervised Machine Learning)
Unsupervised learning is where you only have input data (X) and no corresponding output variables.
The goal for unsupervised learning is to model the underlying structure or distribution in the data in order to learn more about the data.
These are called unsupervised learning because unlike supervised learning above there is no correct answers and there is no teacher. Algorithms are left to their own devises to discover and present the interesting structure in the data.
Unsupervised learning problems can be further grouped into clustering and association problems.
Clustering(聚类): A clustering problem is where you want to discover the inherent groupings in the data, such as grouping customers by purchasing behavior.
Association: An association rule learning problem is where you want to discover rules that describe large portions of your data, such as people that buy X also tend to buy Y.
摘自:https://machinelearningmastery.com/supervised-and-unsupervised-machine-learning-algorithms/
